Fishes come in all shapes and sizes, and they can be found in fresh and saltwater. Though they live in different environments, they all have one common need: to breathe. But how do fish breathe underwater?
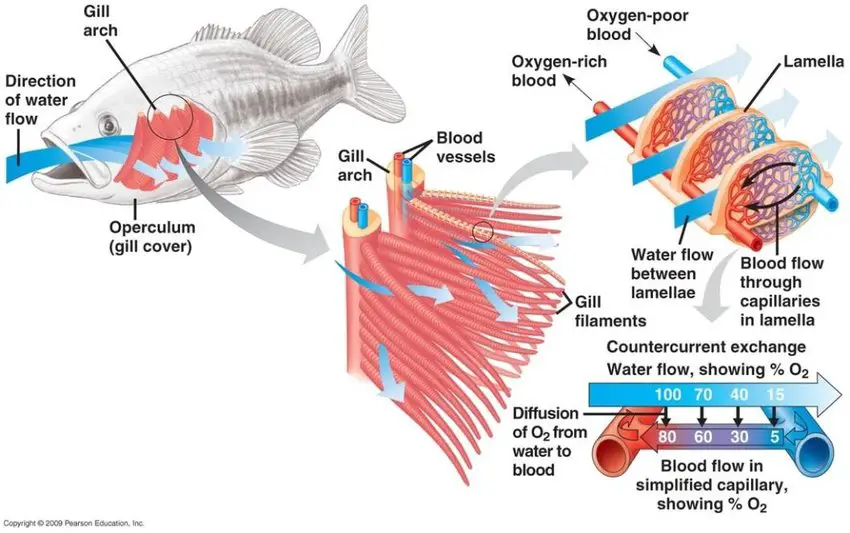
Fish breathe through a system of gills that extract oxygen from the water and excrete carbon dioxide.
Oxygen from the water is absorbed through the gills and passed to the fish’s bloodstream. The carbon dioxide produced by the fish is expelled through the gills.
What Does A Fish Breathe
Fish breathe oxygen from the water to support their aerobic respiration. Gills are thin sheets of tissue that line the fish’s head and operculum (gill cover) help to take dissolved oxygen from water.
Water is drawn in through the mouth and over the gills, where it is expelled through the operculum.
As water passes over the gills, oxygen is absorbed into the bloodstream while carbon dioxide is released.
Fish can vary the amount of water passing over their gills by opening and closing their mouth and operculum.
Some fishes, like lungfish, can also breathe air; they have a special organ called a lung that allows them to do so.
How Do Fish Breath Oxygen In Water
Fish breathe in water by extracting oxygen from the water through their gills. Fish use their gills to extract oxygen from water and excrete carbon dioxide.
The gills are located on the sides of the fish’s head and have a large surface area that allows for a lot of oxygen absorption.
Gills are thin sheets of tissue that have a large number of tiny blood vessels called capillaries. These capillaries are very thin and allow oxygen to diffuse into the blood, and carbon dioxide to diffuse out into the water.
Diffusion is the process of molecules moving from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This process occurs as a result of random motion and collisions between molecules.
The rate of diffusion depends on the concentration gradient, the size of the molecule, and the temperature.
So How does diffusion occur? Random collisions between molecules cause them to move in all directions. This movement continues until the molecules reach a state of equilibrium, meaning that the concentration is equal on both sides of a barrier.
The rate at which oxygen is exchanged between the water and the blood of fish is determined by the difference in concentration between the two environments.
What Happens if There’s Not Enough Oxygen in the Water
If there is not enough oxygen in the water, fish and other aquatic life will die. The dissolved oxygen levels are important to fish because they need it to breathe.
The optimum dissolved oxygen level for fish is 5-8 ppm. If the levels get too low, the fish will start to suffocate.
The low dissolved oxygen conditions are caused by a variety of factors, such as algae blooms, turbidity, pollution, and thermal stratification.
When these events occur, the dissolved oxygen levels in the water drop to dangerously low levels, leading to the suffocation of fish.
In order to prevent this from happening, it is important to understand the causes of hypoxia and anoxia and take steps to mitigate them.
Hypoxia in Fish
Hypoxia, a condition in which there is an inadequate supply of oxygen to meet the metabolic needs of an organism, can occur in both air and water environments.
In aquatic systems, hypoxia is often caused by low dissolved oxygen (DO) levels (below 1-2 mg/L) due to factors such as algal blooms and thermal stratification.
Fish and other aquatic organisms are particularly sensitive to hypoxic conditions and can succumb to its effects within minutes to hours.
Hypoxia can also have indirect impacts on aquatic ecosystems by altering the food web and creating dead zones.
Anoxia in Fish
Anoxia is a condition of water in which there is an insufficient supply of dissolved oxygen (less than 0.01 mg/L) for aquatic life. This can be caused by factors such as low water levels, pollutants, and climate change.
When fish are exposed to anoxic conditions, they can experience severe difficulty breathing.
If left untreated, this can lead to death. Anoxia is a major concern for fish populations and poses a serious threat to their survival.
Why Can’t Fish Breathe Out of Water
Fishes cannot breathe out of water because they have no lungs like other terrestrial animals. Instead, they rely on their gills to take in oxygen from the water and release carbon dioxide.
Fishes must stay in the water to breathe; if they were to leave the water, they would suffocate.
Fishes Have Air Breathing Organ
Few fishes have an accessory breathing organ called the labyrinth organ. This organ is used to breathe air and it is located in the fish’s head.
The labyrinth organ helps the fish get more oxygen from the air and it also helps to keep the fish moist for a long time out of the water.
When you go fishing, you might be surprised to know that the fish you’re trying to catch has an air-breathing organ.
This organ is important for fish that live in shallow water because they need to be able to breathe air when they are out of the water.
Some fish, such as koi, and catfishes use their labyrinth organ to navigate their way home after swimming in saltwater.
FAQs
Do Fish Breathe Air?
No, fish do not breathe air. Fish extract oxygen from the water through their gills.
The water enters the gills and flows over small blood vessels called capillaries. Oxygen from the water passes through the capillaries and into the fish’s bloodstream.
Do Fish Have Lungs?
Fish do not have lungs in the sense that humans do. Fish are a class of vertebrates that live in water and breathe through gills.
Fish use their gills to extract oxygen from the water and expel carbon dioxide. Gills are lined with capillaries that allow the exchange of gases between the fish’s blood and the surrounding water.
Is Fish Air Bladder Use For Breathing?
The air bladder, also known as the gas bladder or swim bladder, is a sac-like organ that helps fish regulate their buoyancy in the water.
It is not used for breathing, contrary to popular belief. The air bladder contains gas-filled chambers that help the fish maintain its equilibrium by adjusting its overall density.
This enables the fish to move up or down in the water column as needed.
Final Words
In conclusion, it is evident that fish have a unique way of breathing that helps them thrive in their aquatic environment.
By understanding how they breathe, we can better appreciate these fascinating creatures and learn more about how they are adapted to their environment.
Related Articles

1 thought on “How Do Fish Breath Underwater?”
Comments are closed.