Looking for a delicious and healthy source of protein? Look no further than freshwater fish!
With so many options out there, it can be hard to decide which one to try first. That’s why we’ve done the research for you and compiled a list of the best freshwater fish to eat.
Whether you prefer a mild flavor or a stronger taste, there’s something on this list for everyone. From the popular and delicious tilapia to the lesser-known but equally tasty rainbow trout, we’ve got you covered.
So why not add some variety to your meals and try one of these delectable freshwater fish today?

What Do You Mean By Freshwater?
Freshwater is a term used to describe water that does not contain salt (less than 0.5 ppt).
This type of water can be found in rivers, lakes, and other bodies of water. Freshwater is often used for drinking and irrigation.
Basically, water is a compound made up of two elements, hydrogen, and oxygen. In its simplest form, it is known as H2O. Of all the water on Earth, 97% is found in the oceans.
The remaining 3% is fresh water, and of that 3%, 2/3 is frozen in glaciers or underground. That leaves us with just 1% of freshwater we can use for drinking, irrigation, and other purposes.
Freshwater vs Saltwater Fish Species
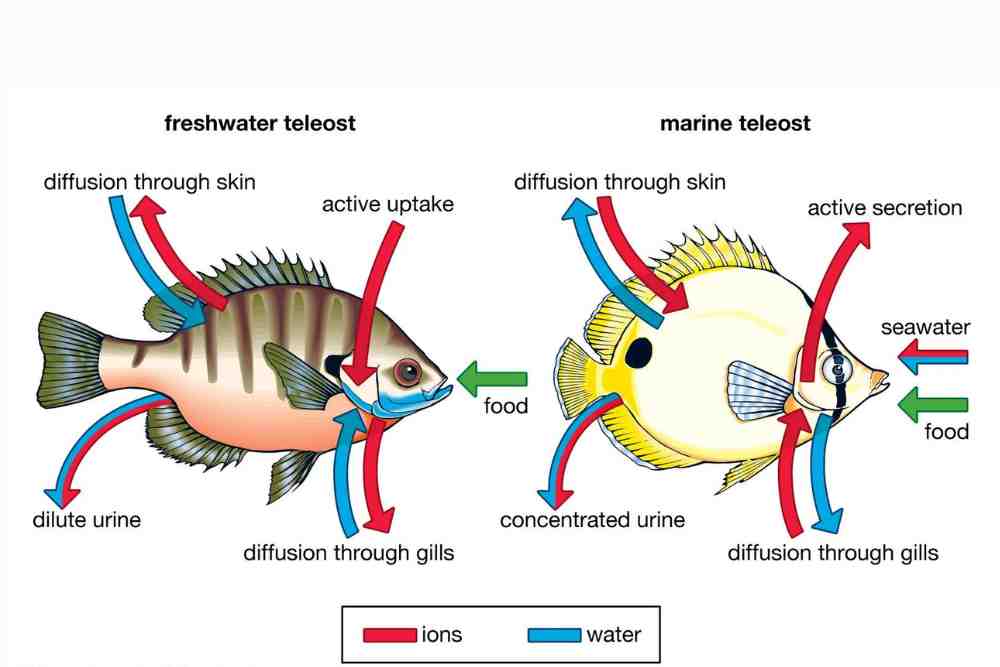
Freshwater and saltwater fish are two distinct types of fish that inhabit different environments and have unique adaptations to survive in their respective habitats.
Freshwater fish species are those that live in bodies of water with a low salt content, such as rivers, lakes, and ponds.
They are adapted to living in these environments and have unique characteristics, such as the ability to extract oxygen from water through their gills.
Freshwater fish often have to contend with changes in water levels, temperature, and oxygen levels. Some common freshwater fish species include trout, bass, catfish, and salmon.
Saltwater fish species, on the other hand, live in bodies of water with a high salt content, such as oceans and seas.
These fish have adapted to living in areas with a high salt concentration and often have different physical features such as a more streamlined body and gills that can extract oxygen from saltwater.
They have the ability to drink saltwater and excrete excess salt through specialized cells in their gills. Some common saltwater fish species include tuna, cod, salmon, and swordfish.
In terms of taste, freshwater fish tend to have a milder flavor than saltwater fish. However, this can vary depending on the species and how they are prepared.
Freshwater fish are also generally easier to farm than saltwater fish, which can make them more readily available and affordable.
The 10 Best Freshwater Fish To Eat | Healthiest Freshwater Fish to Eat
Did you know that there are over 32,000 types of fish in the world and almost 18,000 of them can be found in freshwater?
Here is short brief of 10 best freshwater fish species with their characters, habitat, taste, nutritive values and economic importance.
1. Trout

You may think you know all about fish, but there are still a lot of tasty seafood options out there.
Trout is a great choice that has been spotted in freshwater lakes and rivers across North America, Europe, Asia-pretty much anywhere with water.
There are many reasons that trout is considered the best freshwater fish to eat. Trout is a great source of protein and has low levels of unhealthy fats.
The trout’s mild flavor profile makes it perfect for those who don’t like their food too salty or strong.
Some people have actually called it “the chicken of fish” because its taste reminds them so much of our furry friends’ meaty flesh.
Trout are typically found in cold, fast-moving water with plenty of covers such as rocks and logs.
They have developed a streamlined body shape and powerful tail muscles to help them move through the water quickly.
I especially love smoked trout because of its exotic flavor from being caught near different rivers or streams around town. Fish that are orange or pink in color tastes the best.
Anglers all have their own preferences for what type of trout they like, including brown, brook, and rainbow trout.
Trout have many preparations, but size may be a factor. For smaller trout, frying is preferred while for larger ones filleting and smoking are also acceptable.
Trout can either be baked or broiled as well as pan-fried to achieve maximum flavor potential.
2. Catfish

Catfish are one of the most popular freshwater fish because they can be found all over the world and have lived on every continent.
Features: Catfish have a scaleless long body that is covered in a thick layer of mucus, which gives them a slimy texture. They have a broad, flattened head and long, barbels or “whiskers” around their mouth, which they use to locate food.
Catfish are caught virtually anywhere across North America, with different species growing to various sizes-some as large as 10 feet long.
Their typical character is long barbels that look like a cat’s hair but function as a sensory system for finding food in murky water or dark places such as caves.
Habitat: Catfish are found in a variety of freshwater habitats, including rivers, lakes, and ponds. They are adaptable fish that can survive in both warm and cool water environments, and are often found in areas with dense vegetation or underwater structures such as logs or rocks.
Taste: Catfish has a mild, sweet flavor and a firm, meaty texture that makes it a popular choice for frying, grilling, and baking. Catfish are bottom-dwelling fish that feed on a variety of prey, including insects, small fish, and plant matter. It has a low-fat content, which makes it a healthier alternative to other types of fish such as salmon or tuna.
Nutritional value: They can be cooked in many different ways, my favorite being frying them into small nuggets that are crispy on the outside and tender inside. Catfish is a good source of protein, vitamin B12, and omega-3 fatty acids, which are important for heart health.
A 3.5-ounce (100-gram) serving of fresh catfish provides (Source: USDA):
- Calories: 105
- Fat: 2.9 grams
- Protein: 18 grams
- Cholesterol: 24%
- Omega-3 fatty acids: 237 mg
- Omega-6 fatty acids: 337 mg
- Sodium: 50 mg
- Thiamine: 15%
- Potassium: 19%
- Vitamin B12: 121%
- Selenium: 26%
- Phosphorus: 24%
Commercial value: Catfish is a popular commercial fish that is widely farmed in the United States and other parts of the world. It is often sold fresh or frozen in supermarkets and fish markets.
3. Bass

The bass is one of the tastiest freshwater fish. The size, clarity, and cleanliness of their habitat all play a part in flavor and taste.
However, anglers don’t care about that as much as they do catching it. They say there’s nothing like hooking up with an elusive 25lb beast on your line to make you feel alive again that thrill keeps them coming back for more time after time.
Bass is a popular fish with many things you can do to it bake, fry, sear, and grill. There are some delicious recipes too.
Bass is not just one of the most popular fish, it’s also a versatile option. In addition, there are many recipes that will help make this an enjoyable meal for the whole family.
4. Crappie

When you go fishing, make sure to capture a few of these fish. Brought up on sunny days and warm water, they have an amazing taste that can’t be beaten.
Eating more fish ensures better health for both the brain and body by helping to fight chronic disease risk factors.
You can fry it or grill it with butter for the most common preparations and there are also recipes like fish pancakes to try out an appetizer variety of crappie.
5. Walleye

It’s a freshwater fish native to Northern USA and Canada. Walleye live in many states across America, often living near muddy water due to their sensitivity toward the light.
It tastes great with some salt, pepper, and lemon juice brushed over it before being put on the grill or pan-seared to perfection.
Many people call walleye the best-tasting fish in freshwater, although yellow perch should also get the same accolades, as they are a smaller cousin.
Most walleye are filleted, but they can be cooked in a variety of ways, including frying, baking, and broiling.
Walleye is a fish that’s not too bony and has a soft texture. It is also low in “fishiness” which makes it easy-to-eat white meat with a mild taste of sweetness.
6. Salmon

Salmon are anadromous fishes that live in both salt and fresh water. They are able to adapt to different environments by changing their coloration and body shape depending on the conditions they are living in.
Salmon is one of the best freshwater fish to eat because it is high in protein. Salmon also has a delicious flavor that many people enjoy. Additionally, salmon is easy to cook, so it is a good choice for those who are new to cooking fish.
In addition, salmon is a good source of protein and vitamin D. Salmon also contains antioxidants that can help protect against cancer and other diseases.
7. Bluegill

There are many reasons why bluegill is one of the best freshwater fish to eat.
Bluegill is a versatile and hardy fish that can be found in many parts of the United States.
The flesh of bluegill is mild-tasting and low in fat, making it a healthy option for a meal.
Bluegill can be caught using a variety of methods, including fishing with a hook and line, bow fishing, or gigging. Additionally, bluegill can be readily found in most grocery stores and restaurants.
The bluegill is one of the best freshwater fish to eat because it’s low in mercury and high in protein.
Bluegills are also popular as a food fish, with their sweet, delicate flesh making them a favorite among many. They are often pan-fried or baked, and their small size makes them ideal for serving as a side dish or snack.
While bluegills may not be the largest or most impressive freshwater fish, they are certainly one of the most common and beloved species in North America. Their popularity among anglers and food enthusiasts alike is a testament to their widespread appeal and enduring charm.
8. Pike
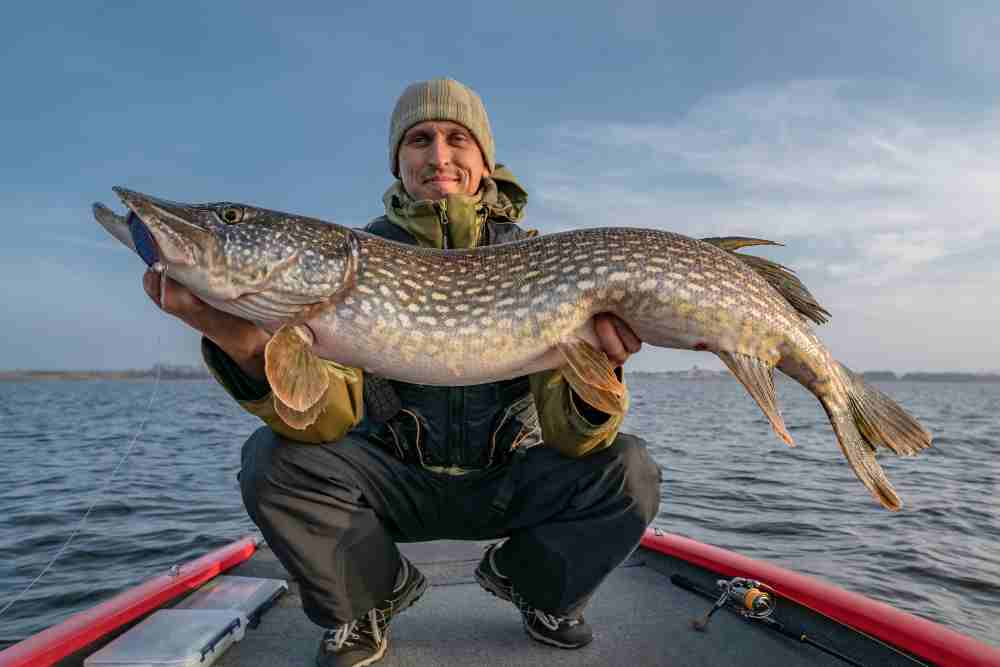

Pike is a popular freshwater fish that is known for its firm, white flesh and mild, sweet flavor.
Characteristics: Pike have long, slender bodies with greenish-brown scales and sharp teeth. They are predatory fish that feed on other fish, and can grow up to three feet in length. Pike are found in freshwater lakes and rivers throughout North America and Europe.
Habitat: Pike prefer shallow, weedy areas of lakes and rivers, where they can ambush their prey. They are most commonly found in clear, cool water with moderate to high levels of dissolved oxygen.
Taste: Pike has a mild, sweet flavor and a firm, white flesh that is similar in texture to chicken. It has a low-fat content, which makes it a healthy choice for those looking to reduce their fat intake. When cooked properly, pike can be a delicious addition to any meal.
Nutritional values: Pike is a good source of protein, vitamin B12, and omega-3 fatty acids, which are important for heart health. It also contains essential minerals such as potassium and magnesium. A 3.5-ounce serving of cooked pike provides approximately 20 grams of protein and 110 calories.
Game fish: Pike is a nutritious and delicious freshwater fish that is a popular choice among anglers and food enthusiasts alike. Its mild flavor and firm texture make it a versatile ingredient that can be used in a variety of dishes, from grilled fillets to fish stews and soups.
9. Perch
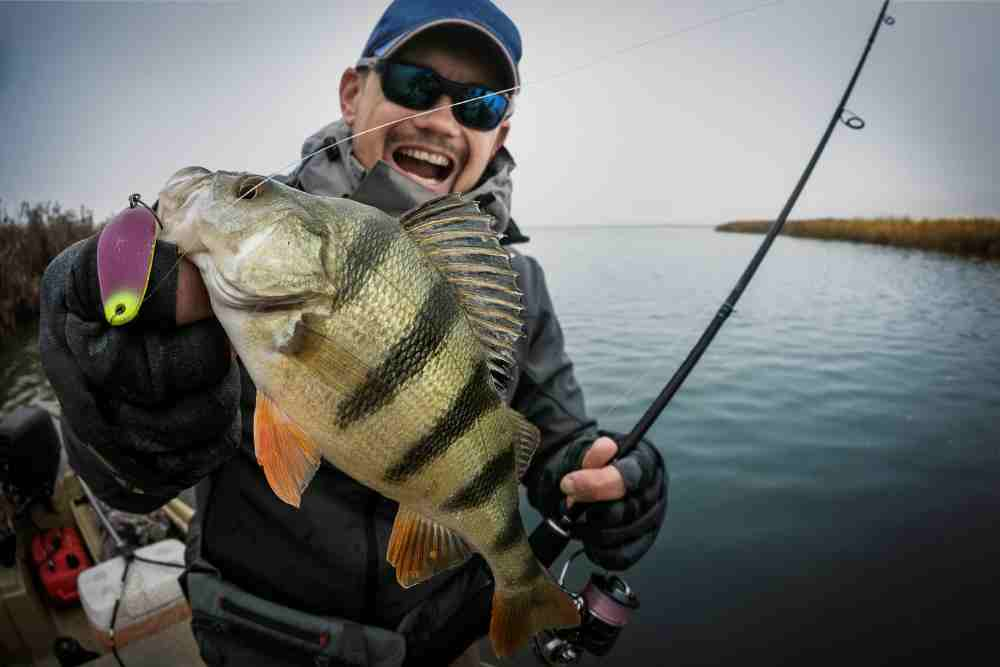

Perch is a popular freshwater fish that is known for its delicate flavor and firm, white flesh.
Characteristics: Perch have a deep, oval-shaped body with greenish-brown scales and sharp spines along their dorsal fin. They are predatory fish that feed on small fish and invertebrates, and can grow up to 10 inches in length. Perch are found in freshwater lakes and rivers throughout North America, Europe, and Asia.
Habitat: Perch prefer clear, cool water with moderate to high levels of dissolved oxygen. They are most commonly found in areas with submerged vegetation or other forms of cover, such as fallen trees or rock formations.
Taste: Perch has a delicate, sweet flavor and a firm, white flesh that is similar in texture to cod or haddock. It is a lean fish with a low-fat content, which makes it a healthy choice for those looking to reduce their fat intake. When cooked properly, perch can be a delicious addition to any meal.
Nutritional values: Perch is a good source of protein, vitamin B12, and omega-3 fatty acids, which are important for heart health. It also contains essential minerals such as potassium and phosphorus. A 3.5-ounce serving of cooked perch provides approximately 20 grams of protein and 90 calories.
Commercial values: Perch is a popular commercial fish, and is often sold fresh or frozen in supermarkets and fish markets. It is also commonly used in the production of fish meal and fish oil for animal feed and dietary supplements.
Overall, perch is a nutritious and delicious freshwater fish that is a popular choice among anglers and food enthusiasts alike.
Its delicate flavor and firm texture make it a versatile ingredient that can be used in a variety of dishes, from pan-fried fillets to fish chowders and stews.
10. Tilapia
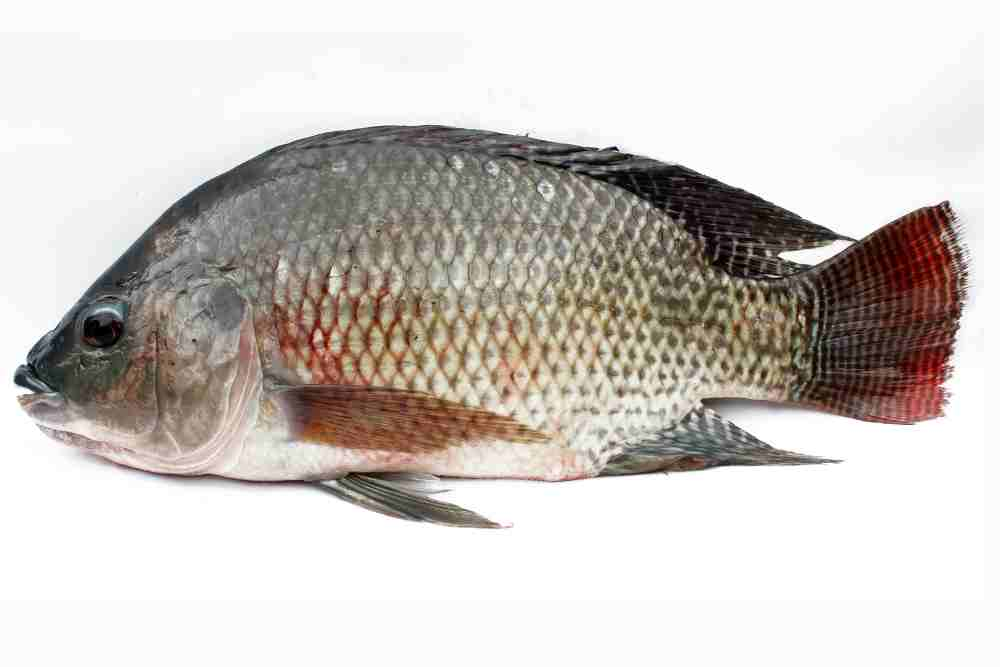

Tilapia commonly known as aquatic chicken is a popular freshwater fish. The consumption and market for tilapia in US is continue growing.
With its mild flavor, low cost, and nutritional benefits, tilapia is likely to remain a popular choice for US consumers looking for a tasty and affordable seafood option.
Characteristics: Tilapia have a deep, compressed body with a silver-gray coloration and iridescent scales. They are omnivorous fish that feed on algae, plankton, and small aquatic animals, and can grow up to 24 inches in length. Tilapia are found in freshwater lakes and rivers throughout Africa, Asia, and the Americas.
Habitat: Tilapia prefer warm water with moderate to high levels of dissolved oxygen. They are most commonly found in areas with abundant vegetation or other forms of cover, such as submerged logs or rocks.
Taste: Tilapia has a mild, sweet flavor and a tender, flaky texture that is similar in taste to cod or catfish. It is a lean fish with a low-fat content, which makes it a healthy choice for those looking to reduce their fat intake. When cooked properly, tilapia can be a delicious addition to any meal.
Nutritional values: A 3-ounce serving contains the following (Source: Everydayhealth)
- Calories: 111
- Protein: 23 g (46 percent DV, or daily value)
- Total fat: 2 g
- Saturated fat: 1 g
- Monounsaturated fat: 1 g
- Polyunsaturated fat: 0.5 g
- Carbohydrates: 0 g
- Fiber: 0 g
- Sugar: 0 g
Commercial value: Tilapia is a popular freshwater fish that is widely consumed in the United States. According to the National Fisheries Institute, tilapia is currently the fourth most consumed seafood in the US, after shrimp, salmon, and canned tuna.
In 2020, the US imported over 247 million pounds of tilapia, making it the largest importer of tilapia in the world. The majority of this tilapia is farmed in countries such as China, Indonesia, and Ecuador, and is sold to US consumers as fresh or frozen fillets.
There are several tilapia farms located throughout the country, particularly in warm southern states such as Florida and Texas.
These farms produce both fresh and frozen tilapia, which is sold to restaurants, supermarkets, and other food retailers.
Freshwater or Saltwater Fish: Which Option is Better for Aquarium?
Deciding whether to keep freshwater or saltwater fish in your aquarium depends on a number of factors, including your experience level, budget, and personal preferences.
Freshwater fish are generally easier to care for and less expensive to set up and maintain than saltwater fish. They are also more tolerant of changes in water chemistry and temperature, making them a good choice for beginner aquarists.
Additionally, there is a wide variety of freshwater fish available, from colorful tropical species to hardy cold-water fish.
Saltwater fish, on the other hand, are known for their stunning colors and unique shapes, and can be a rewarding challenge for experienced aquarists.
They require a more specialized setup and equipment, including a protein skimmer and high-quality lighting, as well as regular water testing and maintenance.
However, with the right setup and care, saltwater aquariums can be a beautiful and vibrant addition to any home.
Freshwater fish are a great option for beginners or those on a tighter budget, while saltwater fish offer a unique and rewarding challenge for experienced hobbyists.
Freshwater Fish vs Saltwater Fish: Which One is Best for Farming?
There are many factors to consider when making this choice, such as the climate, water availability, and the types of fish that are being farmed.
Freshwater fish farming is most commonly done in warm climates where there is an abundance of fresh water. Saltwater fish farming is most commonly done in colder climates where there is an abundance of salt water.
“According to FAO Freshwater fish make up 60% of global fish consumption, while saltwater fish make up 40%. In terms of global aquaculture production by volume, freshwater fish account for 90%, while saltwater fish account for 10%.“
Freshwater Fish Farming: Freshwater fish are generally easier to farm than saltwater fish, as they are more tolerant of changes in temperature, salinity, and water quality.
They can be farmed in a variety of settings, including ponds, tanks, and recirculating aquaculture systems. Some of the most commonly farmed freshwater fish include tilapia, catfish, and trout.
Benefits of Freshwater Fish Farming:
- Lower operating costs: Freshwater fish farming tends to be less expensive than saltwater fish farming, as it requires less infrastructure and equipment.
- Higher stocking densities: Freshwater fish can be stocked at higher densities than saltwater fish, which means that more fish can be raised in a smaller space.
- Lower feed costs: Freshwater fish tend to be more efficient at converting feed into body mass, which means that they require less feed overall.
Saltwater Fish Farming: Saltwater fish farming, also known as mariculture, involves farming fish in ocean or coastal environments. Some of the most commonly farmed saltwater fish include salmon, tuna, and sea bass.
Benefits of Saltwater Fish Farming:
- High market value: Saltwater fish tend to be more valuable than freshwater fish, as they are often considered a luxury food item.
- Less susceptible to disease: Saltwater fish are more resistant to diseases and parasites than freshwater fish.
- Sustainable farming practices: Saltwater fish farming can be done using sustainable practices such as offshore farming, which can help to reduce the impact on wild fish populations. Saltwater fish tend to grow larger and faster than freshwater fish, making them a more lucrative option for farmers.
- Strong demand: There is a strong and growing demand for saltwater fish around the world, particularly in countries such as Japan and China.
What are the Boneless Freshwater Fish to Eat?
There are several boneless freshwater fish species that are popular for consumption due to their mild, delicate flavor and lack of small, fine bones that can be difficult to remove.
Here are some examples:
Tilapia: This is a mild, white-fleshed fish that is widely available and popular for its versatility in cooking. Tilapia is also low in fat and calories, making it a healthy choice.
Catfish: Catfish has a firm texture and mild flavor, and is a popular choice for frying or grilling. Some catfish species have small bones, so it’s important to choose boneless fillets or carefully remove any bones before cooking.
Trout: Trout has a delicate, flaky texture and mild flavor, and is often found in streams and lakes throughout North America.
Perch: Perch is a small, sweet-tasting fish that is often found in freshwater lakes and streams. It has a firm texture and is often fried or grilled.
Walleye: Walleye is a popular game fish in North America and has a delicate, flaky texture and mild flavor. It’s often found in cold-water lakes and rivers and is a good source of protein.
FAQs
Is freshwater fish safe for keto?
Freshwater fish is safe for keto. In fact, it’s a great source of protein and healthy fats, both of which are essential on the keto diet.
Plus, fish is low in carbs and calories, making it a perfect food for people who are trying to lose weight.
Just be sure to choose fish that are low in mercury, such as salmon, trout, and cod. And avoid fried fish or those with high levels of unhealthy fats.
Do freshwater fish have mercury?
Yes, some freshwater fish can contain mercury, just like saltwater fish. Mercury is a toxic metal that can accumulate in the tissues of fish, particularly larger predatory species.
When humans consume fish that contain high levels of mercury, it can potentially lead to health problems such as neurological damage, particularly in developing fetuses and young children.
It’s important to check with your local health department or environmental agency for information on which species of freshwater fish are safe to eat in your area, and to follow any guidelines they provide for consumption.
To reduce the risk of consuming mercury, it’s also recommended to remove the skin and fat from fish, as these are the parts that tend to accumulate higher levels of contaminants.
Additionally, it’s best to avoid eating fish caught in polluted waters, as these are more likely to contain higher levels of mercury and other harmful substances.
Are freshwater fish poisonous?
Some species of freshwater fish can be poisonous if not prepared or cooked properly, but not all freshwater fish are poisonous.
One example of a potentially poisonous freshwater fish is the pufferfish, which contains tetrodotoxin, a powerful neurotoxin that can be deadly if ingested.
Other freshwater fish, such as certain species of catfish, can have venomous spines that can cause painful injuries if handled improperly.
However, the flesh of these fish is not poisonous, and they can be safely consumed once the spines are removed.
In general, freshwater fish are safe to eat as long as they are properly prepared and cooked to eliminate any potential pathogens or toxins.
It’s always important to follow proper food safety guidelines, such as storing and cooking fish at the appropriate temperatures and washing hands and surfaces thoroughly before and after handling raw fish.
Is freshwater fish good to eat?
Yes. The best types of freshwater fish to eat include salmon, trout, and bass. These fish are all high in protein and omega-3 fatty acids, which are important for maintaining a healthy diet.
They also tend to be low in mercury, making them a safer choice for people who are concerned about their health.
Which is the best-tasting fish in the USA?
One of the best-tasting fish in the USA is salmon. Salmon is a type of trout that is typically found in cold water environments. Salmon is a very healthy fish and it is loaded with omega-3 fatty acids. It also has a delicious flavor that most people enjoy.
Another great-tasting fish is tuna. Tuna is a type of saltwater fish that can be found in many different parts of the world.
Tuna has a firm texture and a mild flavor that most people enjoy. It also contains high levels of omega-3 fatty acids, making it a healthy choice for dinner.
What are the boneless freshwater fish to eat?
One such option is catfish. Other popular boneless fish options include tilapia, perch, and cod. They can be found at most grocery stores and are easy to prepare.
All of these fish are low in fat and calories and are a healthy alternative to red meat. They also contain high levels of omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health and cognitive function.
Is freshwater fish considered seafood?
The answer to this question is no, freshwater fish are not considered seafood. Seafood is defined as any type of fish that lives in salt water, so freshwater fish are not included in this category.
This means that items like salmon and trout, which are typically found in rivers and lakes, are not considered to be seafood. While they may share some similarities with saltwater fish, they have different dietary needs and behaviors that set them apart.
For example, salmon migrate upstream to spawn, while trout typically stay in one location their entire lives.
What happens to saltwater fish in freshwater?
Saltwater fish are able to survive in freshwater, but they can’t live in it permanently. When a saltwater fish is placed in fresh water, its body will start to absorb the freshwater. This causes the salt concentration in the fish’s blood and tissues to decrease.
The freshwater will also dilute the fish’s digestive juices, making it harder for the fish to digest food. If a saltwater fish stays in fresh water for too long, its body will eventually absorb so much freshwater that it will die.
Which is the most common freshwater fish in North America?
The most common freshwater fish in North America is the bluegill. Bluegills are part of the sunfish family and are found throughout the United States and Canada.
These small, colorful fish are popular among anglers due to their abundance and willingness to take bait.
Bluegills are typically found in shallow waters such as ponds, lakes, and slow-moving streams, where they feed on insects, small fish, and crustaceans.
6 thoughts on “The 10 Best Freshwater Fish To Eat”
Comments are closed.